Papers
Info
Deep Learning-Based River Flow Forecasting with MLPs: Comparative Exploratory Analysis Applied to the Tejo and the Mondego Rivers 
Abstract: This paper presents an innovative service for river flow forecasting and its demonstration in two dam-controlled rivers in Portugal, Tejo, and Mondego rivers, based on using Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) models to predict and forecast river flow. The main goal is to create and improve AI models that operate as remote services, providing precise and timely river flow predictions for the next 3 days. This paper examines the use of MLP architectures to predict river discharge using comprehensive hydrological data from Portugal
Year: 2025
Number Pages:
27p..
Author(s): Jesus, G.; Korani, Z.; Alves, E.; Oliveira, A.
: MDPI Journal (Sensors)
Editor: MDPI
Volume:
Revista Sensors.
Keywords: SNIRH; MLP;; Deep learning;; Artificial intelligence;; River flow forecasting;
Info
Guiding Evacuees to Improve Fire Building Evacuation Efficiency: Hazard and Congestion Models to Support Decision Making by a Context-Aware Recommender System 
Abstract: Fires in large buildings can have tragic consequences, including the loss of human lives.Despite the advancements in building construction and fire safety technologies, the unpredictablenature of fires, particularly in large buildings, remains an enormous challenge. Acknowledging theparamount importance of prioritising human safety, the academic community has been focusingconsistently on enhancing the efficiency of building evacuation. While previous studies have inte-grated evacuation simulation models, aiding in aspects such as the design of evacuation routes andemergency signalling, modelling human behaviour during a fire emergency remains challenging dueto cognitive complexities. Moreover, behavioural differences from country to country add anotherlayer of complexity, hindering the creation of a universal behaviour model. Instead of centring onmodelling the occupant behaviour, this paper proposes an innovative approach aimed at enhancingthe occupants
Year: 2023
Number Pages:
22p.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Journal MDPI
Editor: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/buildings
Volume:
Buildings 2023, 13, 3038.
Keywords: context-aware recommender system; multi-agent recommender system; building evacuation efficiency; Internet of Things; human behaviour; fire building evacuation
Info
Model-driven engineering techniques and tools for machine learning-enabled IoT applications: a scoping review 
This paper reviews the literature on model-driven engineering (MDE) tools and languages for the internet of things (IoT). Due to the abundance of big data in the IoT, data analytics and machine learning (DAML) techniques play a key role in providing smart IoT applications. In particular, since a significant portion of the IoT data is sequential time series data, such as sensor data, time series analysis techniques are required. Therefore, IoT modeling languages and tools are expected to support DAML methods, including time series analysis techniques, out of the box. In this paper, we study and classify prior work in the literature through the mentioned lens and following the scoping review approach. Hence, the key underlying research questions are what MDE approaches, tools, and languages have been proposed and which ones have supported DAML techniques at the modeling level and in the scope of smart IoT services.
Year: 2023
Number Pages:
27p.
Author(s): Korani, Z.; Moin, A.; Silva, A.; Ferreira, J.
: Sensors
Editor: MDPI
Volume:
Volume 23, Issue 3.
Keywords: scoping review; literature review; time series; data analytics and machine learning; internet of things; model-driven engineering
Info
Context-Based Multi-Agent Recommender System, Supported on IoT, for Guiding the Occupants of a Building in Case of a Fire 
Abstract: The evacuation of buildings in case of fire is a sensitive issue for civil society that alsomotivates the academic community to develop and study solutions to improve the efficiency ofevacuating these spaces. The study of human behavior in fire emergencies has been one of the areasthat have deserved the attention of researchers. However, this modeling of human behavior is difficultand complex because it depends on factors that are difficult to know and that vary from countryto country. In this paper, a paradigm shift is proposed which, instead of focusing on modeling thebehavior of occupants, focuses on conditioning this behavior by providing real-time information onthe most efficient evacuation routes. Making this information available to occupants is possible witha solution that takes advantage of the growing use of the IoT (Internet of Things) in buildings to helpoccupants adapt to the environment. Supported by the IoT, multi-agent recommender systems canhelp users to adapt to the environment and provide the occupants with the most efficient evacuationroutes. This paradigm shift is achieved through a context-based multi-agent recommender systembased on contextual data obtained from IoT devices, which recommends the most efficient evacuationroutes at any given time. The obtained results suggest that the proposed solution can improve theefficiency of evacuating buildings in the event of a fire; for a scenario with two hundred peoplefollowing the system recommendations, the time they take to reach a safe place decreases by 17.7%.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
30pp.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Journal Electronics (https://www.mdpi.com/journal/electronics)
Editor: MDPI
Volume:
Electronics 2022, 11, 3466..
Keywords: building occupant guidance; occupant behavior conditioning; ontologies; fire building evacuation; IoT
Info
Enhancing a coastal territorial vulnerability index: anticipating the impacts of coastal flooding with a local scale approach 
The coastal zone of mainland Portugal is characterized by its morpho-sedimentary diversity such as estuaries, lagoons, barrier islands, beaches, dunes and cliffs. The high population density and the multiplicity of land use, occupation and activities, makes it an area of great national strategic value. This transforms the coastal zone into a multi-hazard zone, where the occurrences related to coastal flooding and overtopping stand out. In the present work, a multidi mensional methodology called Coastal Territorial Vulnerability Index (CTVI) was developed and applied in three selected areas with a historical record of coastal impacts, to analyze, evaluate and interpret the local vulnerability. The methodology considers four components of coastal territorial vulnerability: morphology, land value, buildings and public areas characteristics. These four components are combined to calculate the CTVI. The results highlight the differences for the analyzed areas, allowing the differentiation of natural and artificial areas. In the natural areas a moderate CTVI predominates, while in the latter, a high and very high CTVI stands out. The results contribute to the development of a comprehensive coastal flood risk assessment and forecasting the impacts
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
442-468pp..
Author(s): Barros, J.; Tavares, A.; Santos, P.; Freire, P.
: Coastal Management
Editor: Taylor & Francis
Volume:
50:5.
Keywords: multidimensional methodology; Vulnerability Index; Coastal Territorial; Vulnerability; Coastal Flooding; Coastal zone
Info
Multispectral Optical Remote Sensing for Water-Leak Detection 
Water losses from water distribution means have a high environmental impact in termsof natural resource depletion (water, energy, ecosystems). This work aims to develop an opticalairborne surveillance service for the detection of water leaks (WADI
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
30p.
Author(s): Krapez, J.-C.; Sanchis Muñoz J; Mazel, C.; Chatelard, C; Déliot, P.; Frédéric, Y.-M.; Barillot,P.; Hélias, F.; Barba Polo J; Olichon,V.; Serra, G.; Brignolles, C.; Carvalho, A.; Carreira, D.; Oliveira
: Sensors
Editor: MPDI
Volume:
22(3), Special Issue Remote Sensing for Forecasting and Monitoring Aquatic Systems.
Keywords: thermal; evaporation; soil moisture; Trapezoid Method;; Triangle Method;; infrared; water leak;; remote sensing
Info
An Ontology for Fire Building Evacuation 
Guiding the building occupants under fire emergency to a safe place is an open research problem. Finding solutions to address the problem requires a perfect knowledge of the fire building evacuation domain. The use of ontologies to model knowledge of a domain allows a common and shared understanding of that domain, between people and heterogeneous systems. This paper presents an ontology that aims to build a knowledge model to better understand the referred domain and to help develop more capable building evacuation solutions and systems. The herein proposed ontology considers the different variables and actors involved in the fire building evacuation process. We followed the Methontology methodology for its developing, and we present all the development steps, from the specification to its implementation with the Protégé tool.
Year: 2021
Number Pages:
pp 975-985.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems book series (LNNS)
Editor: Proceedings of Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology
Volume:
216.
Keywords: Knowledge representation; Ontologies; Fire emergency; Ontology development; Knowledge model; Ontology; Fire building evacuation
Info
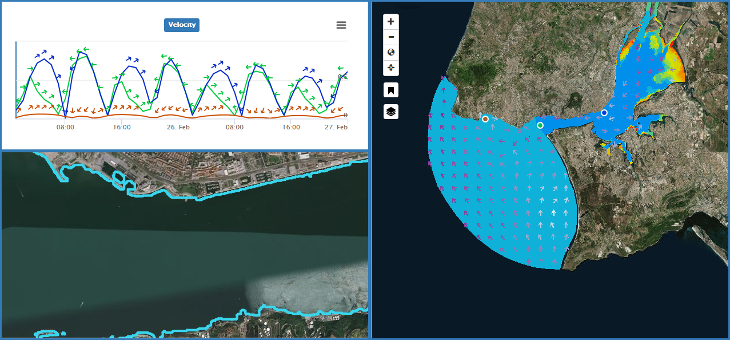
Forecasting contrasting coastal and estuarine hydrodynamics with OPENCoastS 
Robust and accurate coastal forecasts require models to represent the relevant processes, prediction computa-tional tools and reliable computational resources. OPENCoastS is a free, open-source WebGIS platform to develop on-demand hydrodynamic forecast systems that started as a simple 2D engine. OPENCoastS provides a visuali-zation and download interface with in-situ and Sentinel satellite data comparison. 2D tidal, 2D wave & current interaction and 3D baroclinic flows are now included, forced by several atmospheric, oceanic and riverine forcings. Four applications demonstrate OPENCoastS
Year: 2021
Number Pages:
--.
Author(s): Oliveira, A.; Fortunato, A. B.; Rodrigues, M.; Azevedo, A.; Rogeiro, J.; Bernardo, S.; Lauvaud, L.; Bertin, X.; Nahon, A.; Jesus, G.; Rocha, M.; Lopes, P.
: Environmental Modelling and Software
Editor: Elsevier
Volume:
143 (não tem número).
Keywords: Baroclinic modeling; Wave and currents modeling; EOSC; Cross-scale; Unstructured grids; SCHISM; Forecast systems
Info
Multi-Agent-Based Recommender Systems: A Literature Review 
Considering the growing volume of information and services available on the web, it has become essential to provide websites and applications with tools, such as recommender systems, capable of helping users to obtain the information and services appropriate to their interests. Due to the complexity of web adaptation and the ability of multi-agent systems to deal with complex problems, the use of multi-agent approaches in recommender systems has been increasing. In the present work, we make a thorough review of the use of multi-agent-based recommender systems. The review shows the diversity of applications of multi-agent systems in recommender systems, namely on what concerns the diversity of domains, different types of approaches and contribution to the performance improvement of the recommender systems.
Year: 2021
Number Pages:
pp 543-555.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems book series (LNNS)
Editor: Proceedings of Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology
Volume:
235.
Keywords: State-of-the-art; Literature review; Survey; Multi-agent systems; Recommender systems
Info
Multi-Hazard WebGIS Platform for Coastal Regions 
The combined action of waves, surges and tides can cause flooding, erosion and dune andstructure overtopping in many coastal regions. Addressing emergency and risk management in theseareas require a combination of targeted campaigns and real-time data that measure all phenomena atstake and can be used to develop comprehensive monitoring platforms. These monitoring platformscan support the development of prediction tools that address all hazards in an integrated way. Herein,we present a methodology focused on multi-hazard coastal alert and risk, and its implementation in atailoredWebGIS platform. The MOSAIC platform offers a one-stop-shop capacity to access in-situ andremote sensing data, and hydrodynamic and morphodynamic predictions, supported by numericalmodels: SCHISM and XBeach. Information is structured on a local observatory scale, with regionalforcings available for the correct interpretation of local hazards effects. This implementation can befurther applied and extended to other coastal zones. The MOSAIC platform also provides access to adetailed database of past hazardous events, organized along several risk indicators, for the westerncoast of Portugal. The combination of features in the platform provides a unique repository of hazardinformation to support end-users for both emergency and long term risk planning actions.
Year: 2021
Number Pages:
16p.
Author(s): Rocha, M.; Oliveira, A.; Freire, P.; Fortunato, A. B.; Nahon, A.; Barros, J.; Azevedo, A.; Oliveira , F.; Rogeiro, J.; Jesus, G.; Martins, R.; Silva-Santos, P. M.; Tavares, A.; Oliveira, J. N.
: MDPI
Editor: Applied Sciences
Keywords: observatories; GIS; forecast systems; remote sensing; hydro-morphodynamic modeling; flood and erosion risk management; web platform
|
Comunicação
Info
A multi-hazard WebGIS platform to share coastal observatories data and model predictions 
The adequate emergency and risk management of flood and erosion in coastalareas requires a combination of comprehensive monitoring networks, accurateprediction tools and information platforms that can convey data andpredictions in a timely and user-friendly way. Herein, we present a novelweb GIS platform for coastal flood and erosion management targeted at areassubject to the combined action of waves, surges and tides. Information foreach coastal region is organized through a coastal observatory concept, andthe information is tailored to the specific characteristics of eachobservatory. Many data types were implemented, including historical andreal-time sensor data and processed remote sensing information obtainedfrom local cameras or satellites. Predictions are based on a chain ofhigh-resolution models that operate from the ocean to the coast, simulatingwave and current hydrodynamics and their interactions, as well asmorphodynamics, based on models FES2014, WW3, SCHISM and XBEACH. The WebGISplatform provides both spatial and temporal information aiming atcharacterizing hazard, vulnerability and risk. The platform is demonstratedthrough the application to a complex observatory in the central WestPortuguese coast, Cova Gala, to address both flooding and erosion concerns.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
2.
Author(s): Oliveira, A.; Rocha, M.; Jesus, G.; Fortunato, A. B.; Nahon, A.; Rogeiro, J.; Freire, P.
Editor: IAHR
Volume:
Não tem.
Keywords: WebGis
Info
A reliable monitoring approach of floods in small and high slope watersheds 
An implementation to instantiate a dependable data quality-orientedmethodology in the Vinhas Creek monitoring network is presented herein.Redundancy was taken as a core aspect of network reliability. In thisinstantiation, we implement several machine learning mechanisms to processmeasurements from the multiple sensors while correlating them according totheir geographical position, monitoring timing and the relevant physicalprocesses involved. As an output, we are able to predict the sensormeasurements and compare them with the actual sensing value obtained in themonitoring network station. Moreover, in case of any sensor failure, one ormore replacement values can be issued. These are important for the correctsimulation of the hydrologic and hydraulic processes of the dendriticwatershed systems and to predict the inundation characteristics such aslevels and flow velocities.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
4841-4847pp.
Author(s): Jesus, G.; Oliveira, A.; Rogeiro, J.; Rodrigues, R.; Fernandes, J. N.
Editor: IAHR
Volume:
Não tem.
Keywords: Data quality; Flash floods; Machine leaming; Dependable monitoring
Info
An Hybrid Methodology for Integrated Flood Forecasting from the Watershed to the Sea 
Flood forecasting in small watersheds is a complex problem, given the stringent time scales to convey accurate alerts in due time and small spatial scales for both atmospheric and water basin domain prediction. The traditional forecast approach, based on a chain of numerical models for meteorological, hydrological and hydraulic processes is not sufficient, requiring the integration with tailored, real-time data to produce accurate inundation maps and provide timely warnings. Herein, we present a new methodology for flash flood forecasting, based on a two-step procedure and on the use of WIFF, a generic forecast framework applied successfully in estuarine and coastal flood forecasting. In this methodology, WIFF executes two procedures in parallel. First, a large-scale approach, based on conventional numerical models, running continuously every day, to detect significant rain events. If a predicted rain event crosses a warning threshold, a second approach is triggered, involving a small-scale data-based model to predict flooding for the following hours, based on real time monitoring networks data and on the use of high performance computing for machine learning-based simulations. For the first step, we are updating the WIFF framework to integrate both hydrological and hydraulic models of the HEC model family (Brunner, 2021). This methodology is being validated in the Ribeira das Vinhas basin, an area prone to torrential floods that inundate the urban area of the city of Cascais, located at the Tagus estuary mouth.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
4941-4946pp.
Author(s): Oliveira, A.; Jesus, G.; Rogeiro, J.; Fernandes, J. N.; Rodrigues, R.
Editor: IAHR
Volume:
Nao tem.
Keywords: High performance computing; Machine learning-based simulations; Hydraulic modelling;; Flood forecast; Real time data
Info
An Ontological Model for Fire Evacuation Route Recommendation in Buildings 
The study of the evacuation of buildings in emergency fire situations has deserved the attention of researchers for decades, particularly regarding the real-time guiding of occupants in their way to exit the building. However, finding solutions to guide the occupants evacuating a building requires a thorough knowledge of that domain. Using ontological models to model the knowledge of a domain allows the understanding of that domain to be shared. This paper presents an ontological model that pretends to reinforce and deepen knowledge of the domain under study and help develop solutions and systems capable of guiding the occupants during a building evacuation. The ontology was developed following the METHONTOLOGY methodology, and for implementation, the Protégé tool was used. The ontological model was successfully submitted to a thorough evaluation process and is publicly available on the Web.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
109-119pp.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Proceedings of Seventh International Congress on Information and Communication Technology
Editor: Springer
Volume:
Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 464.
Keywords: Internet of things; Ontology; Fire route recommendation; Knowledge representation; Ontological model
Info
Automatic identification of the wave runup line from camera images 
We propose a novel methodology for an automated coastline runup detection fromhigh-resolution remote camera images. As part of a multi-source integrated flood riskassessment platform, this methodology will further improve the characterization of the beachhydrodynamics and define automated procedures for the surveillance of coastal overtoppingand overwash.
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
45-46pp.
Author(s): Martins, R.; Azevedo, A.; Jesus, G.; Oliveira, A.; Fortunato, A. B.; Oliveira , F.; Nahon, A.; Freire, P.
: Livro de Resumos da 6ª Conferência Morfodinâmica Estuarina e Costeira
Editor: LNEC
Keywords: MOSAIC.pt; runup detection; high-resolution; coastline; camera
Info
Geometric and Physical Building Representation and Occupant 
Building evacuation simulation allows for a better assessment of fire safety conditions in existing buildings, which is why it is of interest to develop an easy-to-use Web platform that helps fire safety technicians in this assessment. To achieve this goal, the geometric and physical representation of the building and installed fire safety devices are necessary, as well as the modelling of occupant movement. Although these are widely studied areas, in this paper, we present two new model approaches, either for the physical and geometric representation of a building or for the occupant
Year: 2022
Number Pages:
761
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: Proceedings of Seventh International Congress on Information and Communication Technology
Editor: Springer
Volume:
Vol 448.
Keywords: Building evacuation; Multi-agent systems; Building representation model; Modelling occupants movement; Cellular automata
Info
A multi-agent system for recommending fire evacuation routes in buildings, based on context snd IoT 
Abstract. The herein proposed research project brings together the area of the multi-agent recommender systems and the IoT and aims to study the extent to which a context-based multi-agent recommender system can contribute to im-proving efficiency in the evacuation of buildings under a fire emergency, recom-mending the most adequate and efficient evacuation routes in real time.
Year: 2019
Number Pages:
343-347pp.
Author(s): Neto, J.; Morais, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.; Leça Coelho, A.
: The PAMS Collection
Editor: Springer
Volume:
CCIS, volume 1047.
Keywords: Fire evacuation routes; Internet of things (IoT); Multi-agent systems; Recommender systems
Info
AQUAMON 
Continuous monitoring of aquatic environments using water sensors is important for several applications related to aquaculture and/or water resources management, as well as for recreational activities. Since sensors are constantly being subjected to potentially strong currents and debris accumulation, and the communication between sensors may be affected by waves and electromagnetic interferences, operating sensors in the water environment presents several chal-lenges to data quality assurance and to dependable monitoring. Thus, it is funda-mental to address these challenges in order to avoid false alarms or ignoring rel-evant events.In this paper we present the AQUAMON project, whose objective is to develop a dependable platform based on WSNs for monitoring in aquatic environments. The project addresses data communication and data quality problems, by per-forming comparative studies of available wireless technologies with respect to aspects with impact on communication quality and deployment cost and propos-ing new data processing approaches to detect sensor and network failures affect-ing data quality and to mitigate the effects of these failures
Year: 2019
Number Pages:
3p.
Author(s): Casimiro, A.; Cecílio, J.; Ferreira, P.; Oliveira, A.; Freire, P.; Rodrigues, M.; Almeida, L.
Editor: fcul
Keywords: Aquatic Environments; Wireless Sensor Network; Dependability
Info
Previsão em tempo real a pedido na costa portuguesa - O serviço opencoasts.pt e sua demonstração na circulação da Ria Formosa 
A necessidade de prever eventos extremos (como tempestades, inundações e galgamentos costeiros) e de antecipar os impactos de acidentes (como derrames de hidrocarbonetos e descargas ilegais) motivou o desenvolvimento pelo LNEC de um sistema de previsão em tempo real e a sua aplicação à costa portuguesa. Designado por WIFF
Year: 2018
Number Pages:
16p.
Author(s): Teixeira, J.; Fortunato, A. B.; Rogeiro, J.; Azevedo, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Oliveira, A.
: APRH
Editor: APRH
Keywords: Infraestruturas computacionais; Cloud; Modelos de malhas não estrutural; Webgis; Circulação costeira; Sistemas de previsão em tempo real
Info
Wadi 
A redução de fugas em grandes redes de distribuição de água foi identificada como um dos desafios do Horizonte 2020, para contribuir para a criação de uma sociedade eficiente em termos hídricos e energéticos e resiliente aos impactos das alterações climáticas.No projeto H2020 WADI desenvolveu-se um conceito inovador para deteção de fugas de água nestas redes. A metodologia WADI consiste na utilização acoplada de dispositivos óticos de monitorização remota, instalados em plataformas aéreas complementares (aviões e drones). Esta metodologia permite uma monitorização precoce das fugas de forma precisa, mesmo em sistemas de difícil acesso, sendo uma alternativa mais eficiente e económica aos métodos locais disponíveis e mais fiável do que a deteção por satélites.A aplicação deste sistema de deteção precoce de fugas vai permitir aumentar a eficiência do uso da água. A metodologia será demonstrada em dois sítios piloto: na região da Provença para desenvolvimento da metodologia e validação da tecnologia, e no empreendimento do Alqueva, para demonstração operacional. A aplicação numa seção da rede de rega deste empreendimento pretende reduzir o consumo de água e também o consumo de energia, dado que toda a água é bombeada neste empreendimento.O sistema WADI foi já aplicado para validação preliminar na infraestrutura da rede de água da Société du Canal de Provence (SCP). A plataforma aérea voou sobre 3 áreas com alto potencial de humidade do solo, para deteção de várias fugas de água criadas artificialmente, validando o procedimento de deteção. Os dados das primeiras campanhas WADI foram já processados para suportar a determinação de comprimentos de onda otimizados para deteção de fugas. O resultado é uma série de mapas de diferentes indicadores que permitem revelar a presença de água (índice de água). Apresenta-se nesta comunicação a metodologia WADI e uma primeira especificação da sua demonstração no empreendimento do Alqueva.
Year: 2018
Number Pages:
11p.
Author(s): Carvalho, A.; Oliveira, A.; Alves, E.
Editor: APRH
Keywords: Aviões tripulados; Drones; Deteção remota de fugas; Eficiência hídrica
|
Books
Info
Advances in Water Resources Technology and Management
N/A
Year: 1994
Author(s): Tsakiris, G.; Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
|
Tese de Doutoramento
Info
A dependability framework for WSN-based aquatic monitoring systems 
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are being progressively used in several applicationareas, particularly to collect data and monitor physical processes.Moreover, sensor nodes used in environmental monitoring applications, suchas the aquatic sensor networks, are often subject to harsh environmental conditionswhile monitoring complex phenomena. Non-functional requirements,like reliability, security or availability, are increasingly important and must beaccounted for in the application development. For that purpose, there is alarge body of knowledge on dependability techniques for distributed systems,which provides a good basis to understand how to satisfy these non-functionalrequirements of WSN-based monitoring applications. Given the data-centricnature of monitoring applications, it is of particular importance to ensure thatdata is reliable or, more generically, that it has the necessary quality.The problem of ensuring the desired quality of data for dependable monitoringusing WSNs is studied herein. With a dependability-oriented perspective,it is reviewed the possible impairments to dependability and the prominentexisting solutions to solve or mitigate these impairments. Despite the varietyof components that may form a WSN-based monitoring system, it is givenparticular attention to understanding which faults can affect sensors, howthey can affect the quality of the information, and how this quality can beimproved and quantified. Open research issues for the specific case of aquaticmonitoring applications are also discussed.One of the challenges in achieving a dependable system behavior is to overcomethe external disturbances affecting sensor measurements and detect thefailure patterns in sensor data. This is a particular problem in environmentalmonitoring, due to the difficulty in distinguishing a faulty behavior fromthe representation of a natural phenomenon. Existing solutions for failuredetection assume that physical processes can be accurately modeled, or thatthere are large deviations that may be detected using coarse techniques, ormore commonly that it is a high-density sensor network with value redundantsensors.This thesis aims at defining a new methodology for dependable data qualityin environmental monitoring systems, aiming to detect faulty measurementsand increase the sensors data quality. The framework of the methodology isoverviewed through a generically applicable design, which can be employed toany environment sensor network dataset.The methodology is evaluated in various datasets of different WSNs, where it isused machine learning to model each sensor behavior, exploiting the existenceof correlated data provided by neighbor sensors. It is intended to explorethe data fusion strategies in order to effectively detect potential failures foreach sensor and, simultaneously, distinguish truly abnormal measurementsfrom deviations due to natural phenomena. This is accomplished with thesuccessful application of the methodology to detect and correct outliers, offsetand drifting failures in real monitoring networks datasets.In the future, the methodology can be applied to optimize the data qualitycontrol processes of new and already operating monitoring networks, and assistin the networks maintenance operations.
Year: 2019
Author(s): Jesus, G.
Keywords: Aquatic monitoring; Machine learning; Fault detection; Data quality; Dependability
Info
Proposta de Sistema de Aviso Multicanal para Emergências 
As autoridades de proteção civil precisam de avisar as populações em situações de perigo, deforma rápida, previsível e atempada. Esta necessidade é particularmente notada, em situaçõesde emergência, como os desastres naturais ou tecnológicos, quando se pretende informar apopulação numa determinada área, das ações que devem executar para limitar os danospotenciais.O envio do aviso à população é habitualmente feito através de contactos porta a porta,altifalantes, sirenes, telefones, rádio, televisão e muitos outros canais de comunicação.Todavia, o envio do aviso através de um único destes canais possui limitações, nãoconseguindo satisfazer todos os requisitos desejáveis.Para a resolução deste problema é proposta e especificada uma arquitetura modular parasistemas de aviso que permite integrar redes de aviso baseadas em distintos canais decomunicação, permitindo o envio do aviso, de forma integrada através de diversos canais. Aadoção desta arquitetura permite construir um sistema de aviso baseado em múltiplos canaisde comunicação, um sistema de aviso multicanal.Para mostrar as possibilidades da arquitetura foram especificadas redes de aviso baseadas emdois canais de comunicação distintos: SMS e televisão digital. Para cada rede de aviso foramidentificadas limitações e propostas soluções, nomeadamente para o aumento da rapidez noenvio do aviso, melhoria na seletividade do envio, utilização da língua preferida dodestinatário, aumento do volume de mensagens que é possível enviar em tempo útil eintrodução de mecanismos de autenticação do aviso.Em particular, foi feita a caraterização analítica de uma rede móvel celular em dois cenáriosde desastre para tentar compreender o comportamento de uma rede de aviso suportada emSMS. Os resultados mostram que o SMS pode ser utilizado nalgumas situações, dependendodo número de pessoas na zona de risco.
Year: 2013
Number Pages:
p222.
Author(s): Fernandes, J. P.
Info
Modelação de dados geográficos aplicada ao planeamento e gestão de recursos hídricos 
A aprovação e implementação da directiva-quadro da água (DQA) e de outras directivas europeias associadas impuseram alterações significativas aos métodos de planeamento e gestão de recursos hídricos e também aos critérios de uso, gestão e partilha de informação geográfica, nomeadamente os que pautam o relato ao sistema europeu de informação sobre águas (WISE) e a contribuição para a infra-estrutura europeia de informação geográfica (INSPIRE).Neste trabalho apresenta-se o processo de desenvolvimento e implementação de um modelo de dados geográficos (MDG) de suporte ao planeamento e gestão de águas superficiais que considerou requisitos técnicos, funcionais e legais. Os requisitos técnicos e funcionais aplicados à informação geográfica foram determinados com base nas normas internacionais aplicadas à especificação de informação geográfica, nomeadamente as da organização internacional de normalização (ISO) e as da infra-estrutura europeia de informação geográfica (INSPIRE). Os requisitos legais foram determinados por diplomas legais europeus e portugueses que estabelecem as metodologias de planeamento e gestão, conjuntos de dados geográficos, métodos de classificação, fluxos de análise, simbologia de apresentação de dados, entre outros.Destacam-se quatro casos de utilização do MDG: i) produção cartográfica; ii) análise espacial e modelação hidrológica e hidráulica; iii) relato ao WISE; e iv) suporte aos produtos resultantes da elaboração dos planos de gestão de região hidrográfica (PGRH).A metodologia utilizada no desenvolvimento do MDG baseou-se nas normas ISO 19103 e 19109, que preconizam quatro fases de desenvolvimento: i) declaração do universo de discurso; ii) modelo conceptual; iii) modelo lógico e iv) modelo físico de dados. Após a implementação do MDG num sistema de gestão de bases de dados geográficos procedeu-se ao seu carregamento com dados, tendo sido testadas e descritas as funcionalidades oferecidas pelo desenho do MDG no âmbito da aplicação ao planeamento e gestão de recursos superficiais.
Year: 2012
Number Pages:
p268.
Author(s): Charneca, N.
Keywords: Águas superficiais; Modelação de dados geograficos
Info
On the stochastic characterization of regional droughts 
N/A
Year: 1981
Author(s): Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
|
Dissertações de Mestrado
Info
PAC:MAN - SISTEMA DE GESTÃO AO RISCO DE ACIDENTES DE POLUIÇÃO EM ZONAS COSTEIRAS 
O efeito da poluição por derrames acidentais nos ecossistemas costeiros motivou a procura e o desenvolvimento de abordagens para planeamento e resposta atempados à emergência com o intuito de proteger os recursos aquáticos. Os sistemas de monitorização da poluição e de modelação existentes são utilizados de forma independente durante acidentes deste âmbito sem a eficácia pretendida. A prevenção do risco de derrame é, habitualmente, feita via planos de contingência com base em estudos simplistas não refletindo o dinamismo da informação nem permitindo o alerta atempado dos gestores costeiros devido ao uso de tecnologia desatualizada.Os sistemas de gestão de risco, testados com sucesso em desastres ambientais e humanitários, demonstram ser soluções promissoras. A sua adequação permite criar sistemas de gestão de risco mais específicos, como riscos de poluição e gestão da resposta á emergência em zonas costeiras. Esta inovação permite conjugar a modelação costeira de vanguarda para análise de risco, a riqueza de informação ambiental existente para a definição de indicadores de condições propícias á ocorrência de derrames e as tecnologias de comunicação. Obtém-se como resultado um conjunto de meios de alerta precoce e resposta mais eficiente e benéfica do ponto de vista da segurança das populações, da capacidade de atuação dos gestores costeiros e da manutenção dos recursos naturais costeiros.A adaptação dos módulos do sistema de gestão de risco de acidentes por rotura de barragens SAGE-B permitiu conceber um novo sistema de gestão de risco de poluição em zonas costeiras que incluiu um sistema de alerta precoce resultante da aplicação dos modelos, um sistema de aviso associado e uma base de dados com os recursos em risco e os meios de resposta à emergência para a análise da vulnerabilidade na Ria de Aveiro, obtendo-se uma nova metodologia genérica de planeamento e resposta para riscos de poluição costeira.
Year: 2012
Number Pages:
p91.
Author(s): Sousa, C.
Keywords: Sistemas tempo-real; Sistemas de informação; Sistema de alerta e aviso; Sistema de gestão de risco
Info
Processo Iterativo de Migração de Dados 
Com a evolução das tecnologias de informação, a migração de dados legados é essencial para garantir o correcto funcionamento das novas aplicações. A eficiência e correcção das aplicações depende, fortemente, da qualidade dos dados armazenados.A criação de processos de migração de dados através da implementação de Software específico é bastante complexa. Por isso, é fundamental disponibilizar mecanismos de apoio à realização de tarefas de tratamento e migração de dados.A framework Ajax disponibiliza vários operadores para limpeza e transformação de dados. Não sendo uma ferramenta exclusivamente orientada para a migração de dados, pretende-se que a sua utilização na migração de um projecto real permita validar a respectiva aplicação. Todas as lacunas dos operadores do Ajax podem, assim, ser preenchidas através do refinamento e extensão da lógica dos operadores, nomeadamente, no suporte à identificação de registos errados e ao carregamento incremental de dados nos sistemas alvo.No âmbito do projecto gestBarragens, desenvolveu-se um processo de migração que inclui o carregamento de um sistema de informação legado e vários sistemas simples relacionados com informação acerca da segurança de barragens de betão em Portugal.
Year: 2008
Author(s): Barateiro, J.
Keywords: Grafo; Limpeza de dados; Qualidade de dados; Etl; Migração
Info
Workflow modeling using UML, Declarative Tools and WEB2.0 
Manual translation of UML diagrams to programmatic code is tedious anderror prone. Many CASE tools allow computer code to be generated fromClass Diagrams, but fewer, if any, allow the transformation of Activity Dia-grams (ADs) in executable and workflow defining computer code.Our project aims at:
Year: 2008
Author(s): Gamito, R.
Keywords: Isco; Uml; Workflow
|
|
|
Programas de Investigação
Info
Digital coast: a scientific proposal for it- based research in coastal regions for the next decade 
This document corresponds to the Research Program and associated Post-Graduation Program elaborated by the author in the scope of the process of certification for the functions of coordination of scientific research, according to Decree-Law no. 124/99, of April 20th. This Research Program identifies several research themes for the next decade related to the application of information technologies in coastal science and innovation of research. The selection of these themes is framed in the scientific national and international context, focused in particular in the activity of LNEC in this area through the research of the Information Technology in Water and Environment research group, led by the applicant, in collaboration with other divisions of the Hydraulics and Environment Department. After a brief overview of the theme and presentation of the rationale for the development of this work, the national and global context for the Program is presented, wrapping up with the presentation of the research strategy for the Information Technology in Water and Environment research group. From this strategy, the two research areas of this Habilitation Program are identified and briefly described. The first area is the creation and development of reliable, cross-scale, multi-process, on-demand coastal forecast framework for oceans to hydrographic basin application, from hydrodynamics to biogeochemistry. The second area is the creation and development of intelligent, high-resolution, user centered and inclusive coastal digital twins. The two following chapters present the state-of-the-art in these two areas, the challenges to be overcome and the general roadmaps for the tools to be developed in the next decade to address the societal challenges in the coastal regions. The two Research Studies are presented next, organized along 19 projects. For each project, the applicant presents the rationale behind it, along with its goals, describes the methodologies for its implementation and the results to be generated. The resources necessary for its implementation along with the expected partnerships and adequate funding sources are also described. Finally, the Post-Graduation Program is presented, providing multiple M.Sc. and Ph.D. education opportunities framed in the previous Research Program. A total of 9 Ph.D. and 6 M.Sc. proposals are presented.
Year: 2022
Author(s): Oliveira, A.
Keywords: Collaboratories; Early-warning systems; Information quality and reliability; Data-based methodologies; Cross-scale modeling; Multi-process; Artificial intelligence; Hybrid forecast systems; Coastal Digital Twins
Info
Decision-support systems in water resources 
N/A
Year: 1991
Number Pages:
152.
Author(s): Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
|
Relatório Científico
Info
Spatial intelligent agent component to reason about prospective routing/place selections (D4.3.1) 
N/A
Year: 2004
Author(s): Gonçalves, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
Info
Evaluation of Existing Information Services 
N/A
Year: 2003
Number Pages:
12.
Author(s): Gonçalves, A.; Dias, E.; Rodrigues, A.
Editor: ******
Info
Multi-Agent Geographic Simulations Based on Interoperable Components 
N/A
Year: 2003
Author(s): Rodrigues, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Grueau, C.
Editor: ******
Info
Relatório Intercalar de Auto-avaliação do Projecto "Tecnologias Avançadas de Tratamento de Informação em Hidráulica e Ambiente" 
Este relatório inclui a auto avaliação intercalar do projecto Tecnologias Avançadas de Tratamento de Informação em Hidráulica e Ambiente do Plano de Investigação Programada do LNEC para 2001-2004. Refere-se ao primeiro biénio desse período e contém dados sobre a actividade desenvolvida em cada um dos estudos do projecto e a sua comparação com o plano.
Year: 2003
Number Pages:
16 p.
Author(s): Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
Info
MacauWaves v2.0: User´s manual 
MacauWaves 1.0 is the first version of a database application created by the Harbours and Beaches Division with the goal of storing, organising and disseminating the available wave data observed in the macao coast. One and a half year after that first release, it was decided to upagrade it. The new modifications focus on security issues and on the dynamic generation of graphics. This report constitutes the User s manual of MacauWaves secind version. It must be seen as a guideline for the installation and the use of the application.
Year: 2002
Number Pages:
43 p.
Author(s): Sousa, R. M.; Santos, M. A.
Editor: ******
Info
Protótipo dum sistema de indução de árvores de decisão, versão beta. 
N/A
Year: 2002
Author(s): Gonçalves, A.
Editor: ******
Seminário sobre A Hidroinformática em Portugal 
Info
Sistema de apoio à gestão de emergência provocada por roturas de barragens. O caso das Barragens do Funcho e do Arade 
Neste relatório, descreve-se o sistema de apoio à decisão para a gestão de crises provocadas pela eventual rotura das barragens do Funcho e do Arade. Este sistema, ainda na fase de protótipo, baseia-se em desenvolvimentos recentes na área das tecnologias de informação e da comunicação de dados, e deverá implementar os Planos de Emergência Interna e Externa para as barragens do caso de estudo.
Year: 2002
Number Pages:
85 p.
Author(s): Santos, M. A.; Rodrigues, A.; Gamboa, M.
Editor: ******
Info
Sistemas de transmissão de dados 
N/A
Year: 2002
Author(s): Fernandes, J. P.
Editor: ******
Info
Windows XP Professional: Instalação manual 
N/A
Year: 2002
Author(s): Fernandes, J. P.
Editor: ******
|
Outro
Info
PAC:MAN
O projecto PAC:MAN é coordenado pela Doutora Anabela Oliveira (LNEC) e inclui uma equipa de investigadores do Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil (Instituição proponente), Centro Interdisciplinar de Investigação Marinha e Ambiental e Universidade de Aveiro. Este projecto tem como objectivos investigar: (i) os dados de acidentes passados para desenvolver e validar um conjunto de indicadores ambientais de condições atmosféricas e oceanográficas propícias à ocorrência de derrames; (ii) a capacidade e eficiência do sistema de modelação de elevada precisão para prevenção e previsão do risco de derrame, incluindo todos os processos de transformação de óleo na zona costeira; (iii) a fiabilidade, vantagens e escalabilidade de um sistema de alerta baseado em novas tecnologias móveis; e (iv) o modocomo estes vários aspectos inovadores podem ser integrados num sistema de gestão de risco para alerta precoce e aviso da ocorrência de derrames nas zonas costeiras. Na fase inicial do projecto foi feita a análise de dados in situ e de deteção remota para acidentes de poluição na plataforma continental Ibérica e zona costeira, para apoiar o desenvolvimento de indicadores de condições propícias à ocorrência de acidentes com embarcações que ultimamente poderão conduzir ao derrame de hidrocarbonetos. Estes indicadores foram validados para a Ria de Aveiro, a qual foi escolhida pela sua enorme importância ambiental e económica. Foi definido um conjunto de cenários, aos quais estão associados os resultados duma análise de vulnerabilidade local. Os cenários foram utilizados para avaliar a capacidade dos modelos detalhados de serem aplicados na análise de risco, e para desenvolver uma nova metodologia de prevenção deste tipo de riscos. Este sistema de modelação de derrames simula os processos relevantes em escalas adequadas e está acoplado com um sistema de modelação da circulação forçada conjuntamente por ondas, correntes evento. A metodologia proposta será a base para um sistema inovador de alerta precoce que combina de modo eficiente as condições ambientais propícias à ocorrência de acidentes com previsões detalhadas do percurso e da transformação das plumas de poluentes. Este sistema de alerta irá alimentar um sistema de aviso, o qual será analisado em termos de eficiência e escalabilidade para números crescentes de utilizadores. Os dois sistemas serão ligados através de um sistema de gestão do risco, adaptado para derrames a partir de um sistema proposto na literatura. Esta infra-estrutura incluirá uma base de dados dos elementos físicos em risco e dos recursos de resposta à emergência, e será customizado para a análise de vulnerabilidade daRia de Aveiro. O resultado final do projecto será uma nova metodologia de planeamento e resposta para riscos de poluição costeira genérica, baseada nas várias ferramentas e análises propostas.
Year: 2014
Number Pages:
24pp.
Author(s): Epifânio, B.
Info
PAC:MAN - Pollution accidents in coastal areas: a risk management system (ref. PTDC/AAC-AMB/113469/2009)
Os impactos dos derrames acidentais das últimas décadas têm impulsionado o desenvolvimento e a implementação de diversas abordagens para planeamento e resposta à emergência de poluição dos meios aquáticos, incluindo sistemas de monotorização da poluição e sistemas de modelação. Os sistemas de gestão d risco, que foram aplicados com sucesso para tsunamis e inundações de rotura de barragens, podem ser usados para providenciar um enquadramento para riscos de poluição que permita a proteção eficaz dos recursos costeiros.Os objetivos do projeto PAC:MAN são investigar: 1) os dados de acidentes passados para desenvolver e validar um conjunto de indicadores ambientais de condições atmosféricas e oceanográficas propícias à ocorrência de derrames; 2)a capacidade e eficiência de sistemas de modelação de elevada precisão para prevenção e previsão do risco de derrame, incluindo todos os processos de transformação do óleo na zona costeira; 3) a fiabilidade, vantagens e escalabilidade de um sistema de alerta baseado em novas tecnologias móveis; 4) a capacidade dos sistemas de tecnologias de informação para integrar e disponibilizar informação ambiental relevante sobre os elementos ecológicos em risco; e 5) o modo como estes vários aspectos inovadores podem ser integrados num sistema de gestão de risco para alerta precoce e aviso da ocorr~encia de um derrame nas zonas costeiras.
Year: 2014
Number Pages:
6pp.
Author(s): Boer, S.
Info
PAC:MAN - Pollution accidents in coastal areas: A risk management system (ref. PTDC/AAC-AMB/113469/2009)
Os impactos dos derrames acidentais das últimas décadas têm impulsionado o desenvolvimento e a implementação de diversas abordagens para planeamento e resposta à emergência de poluição e sistemas de modelação.Os sistemas de gestão de risco, que foram aplicados com sucesso para tsunamis e inundações de rotura de barragens, podem ser usados para providenciar um enquadramento para riscos de poluição que permita a proteção eficaz dos recursos costeiros. Os objetivos do projeto PAC:MAN são investigar:1) os dados de acidentes passados para desenvolver e validar um conjunto de indicadores ambientais de condições atmosféricas e oceanográficas propícias à ocorrência de derrames;2) a capacidade e eficiência de sistema de modelação de elevada precisão para prevenção e previsão do risco de derrame, incluindo todos os processos de transformação do óleo na zona costeira; 3) a fiabilidade, vantagens e escalabilidade de um sistema de alerta baseado em novas tecnologias móveis; 4) a capacidade dos sistemas de tecnologias de informação para integrar e disponibilizar informação ambiental relevante sobre os elementos ecológicos em risco; 5)o modo como estes vários aspectos inovadores podem ser integrados num sistema de gestão de risco para alerta precoce e aviso da ocorrência de um derrame nas zonas costeiras.
Year: 2014
Number Pages:
6pp.
Author(s): Rogeiro, J.
Info
Ficheiro de Substituição
N/A
Year: 2007
Author(s): Gamito, R.
Info
Risco e gestão de crises em vales a jusante de barragens
N/A
Year: 1998
Author(s): Quintela, A.; Pinheiro, A.; West, C.; Gamboa, M.
Editor: ******
|
 Scientific Instrumentation Centre
Scientific Instrumentation Centre
 Scientific Instrumentation Centre
Scientific Instrumentation Centre

